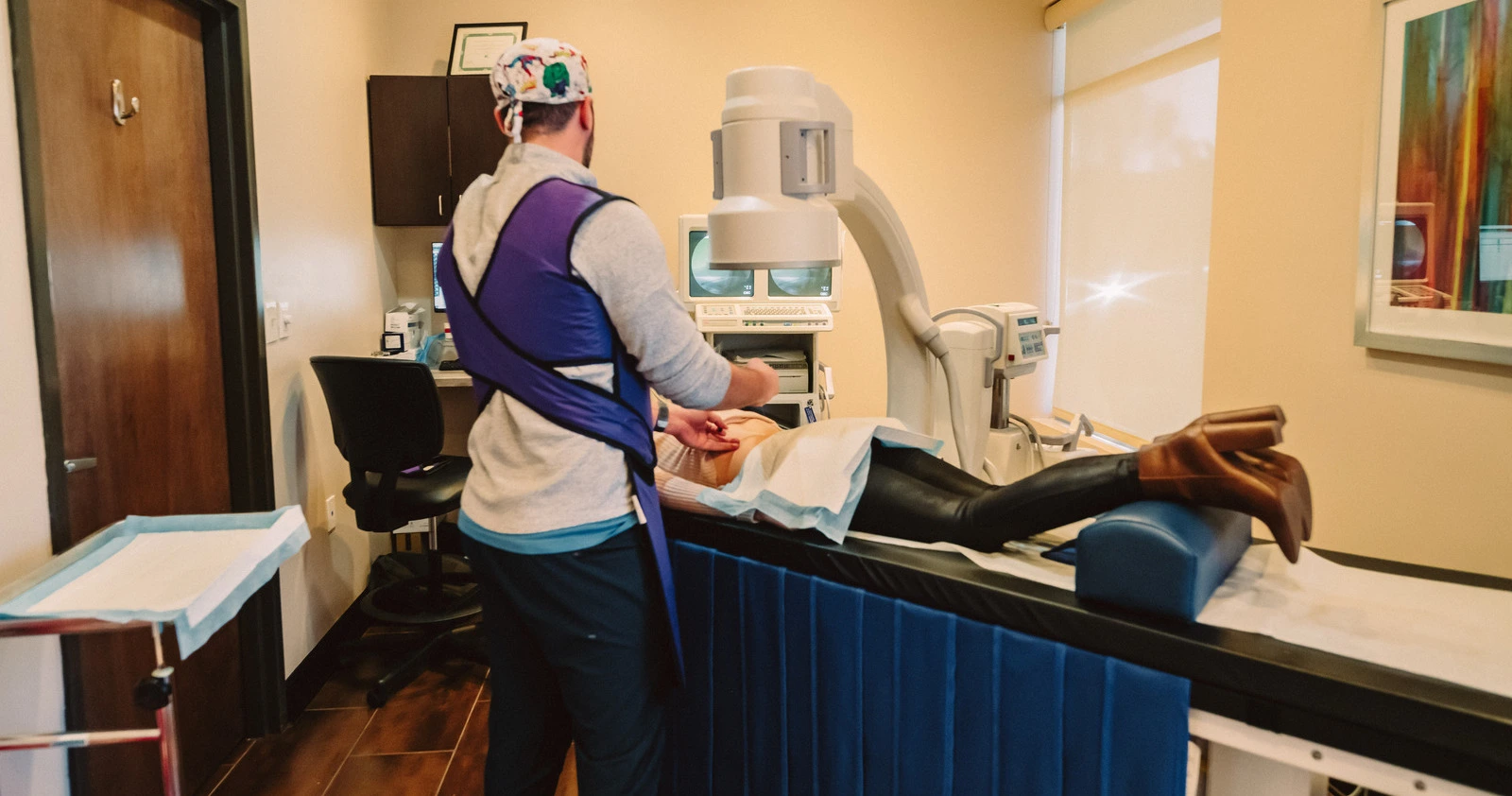
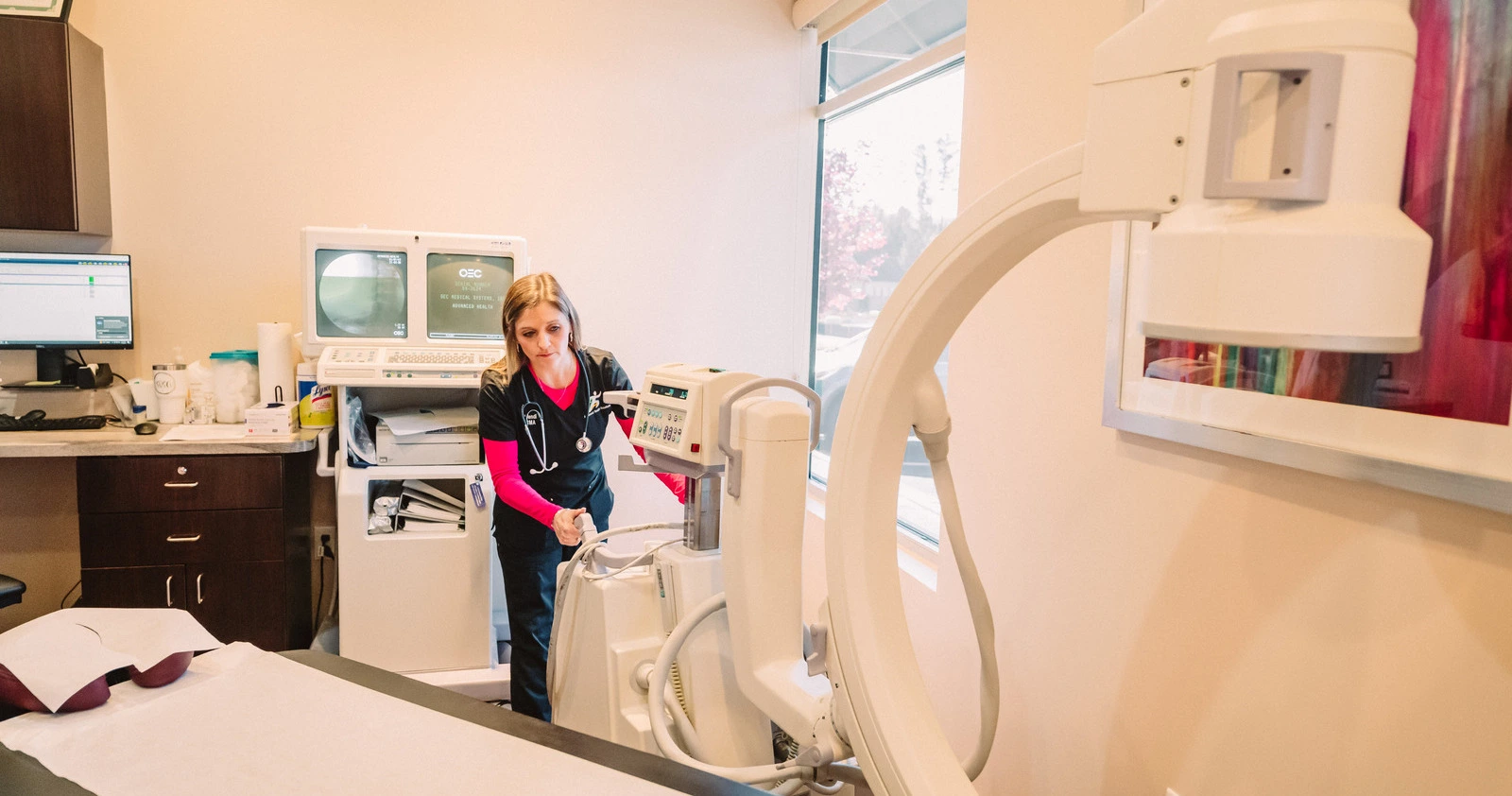
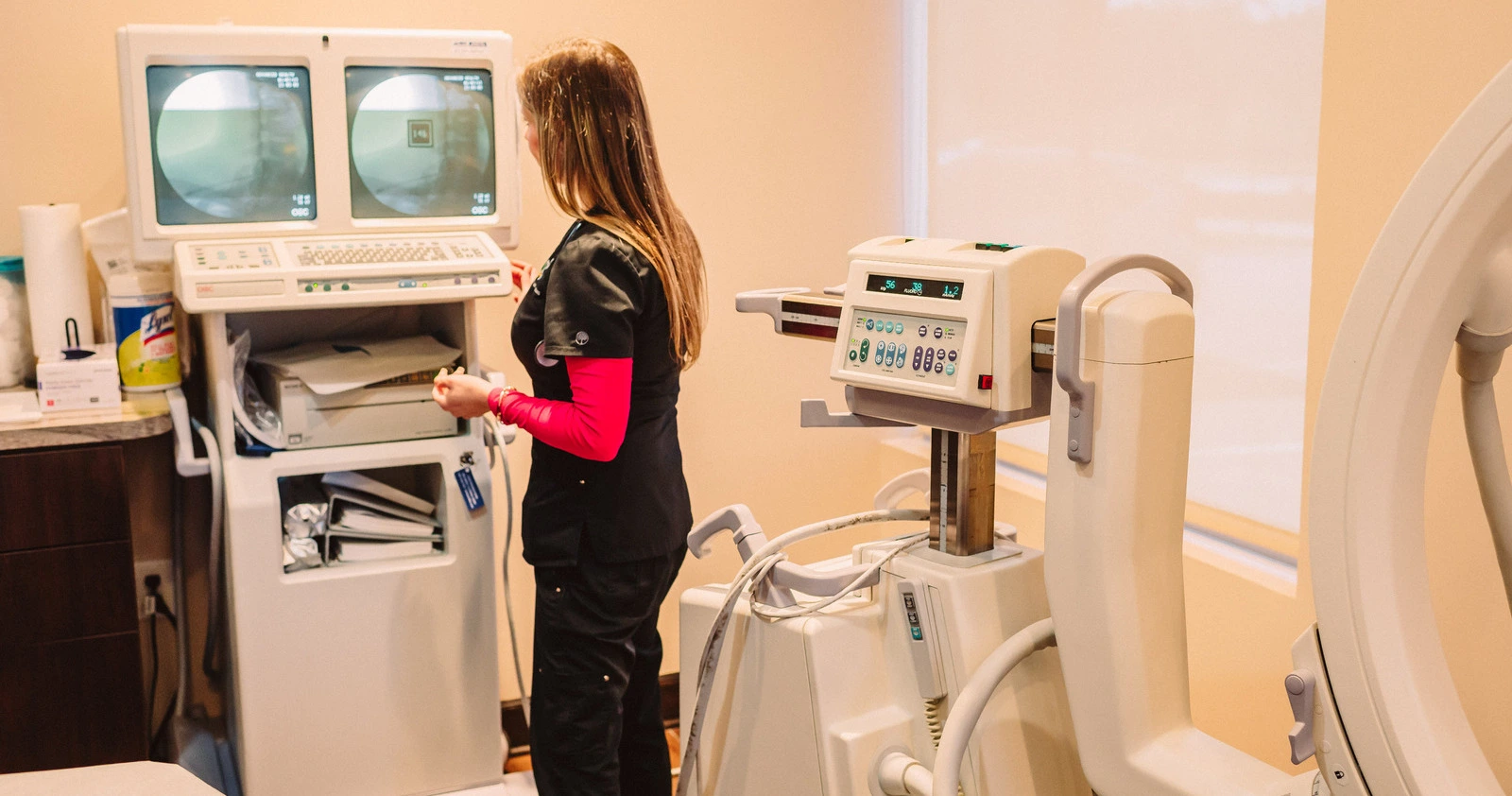
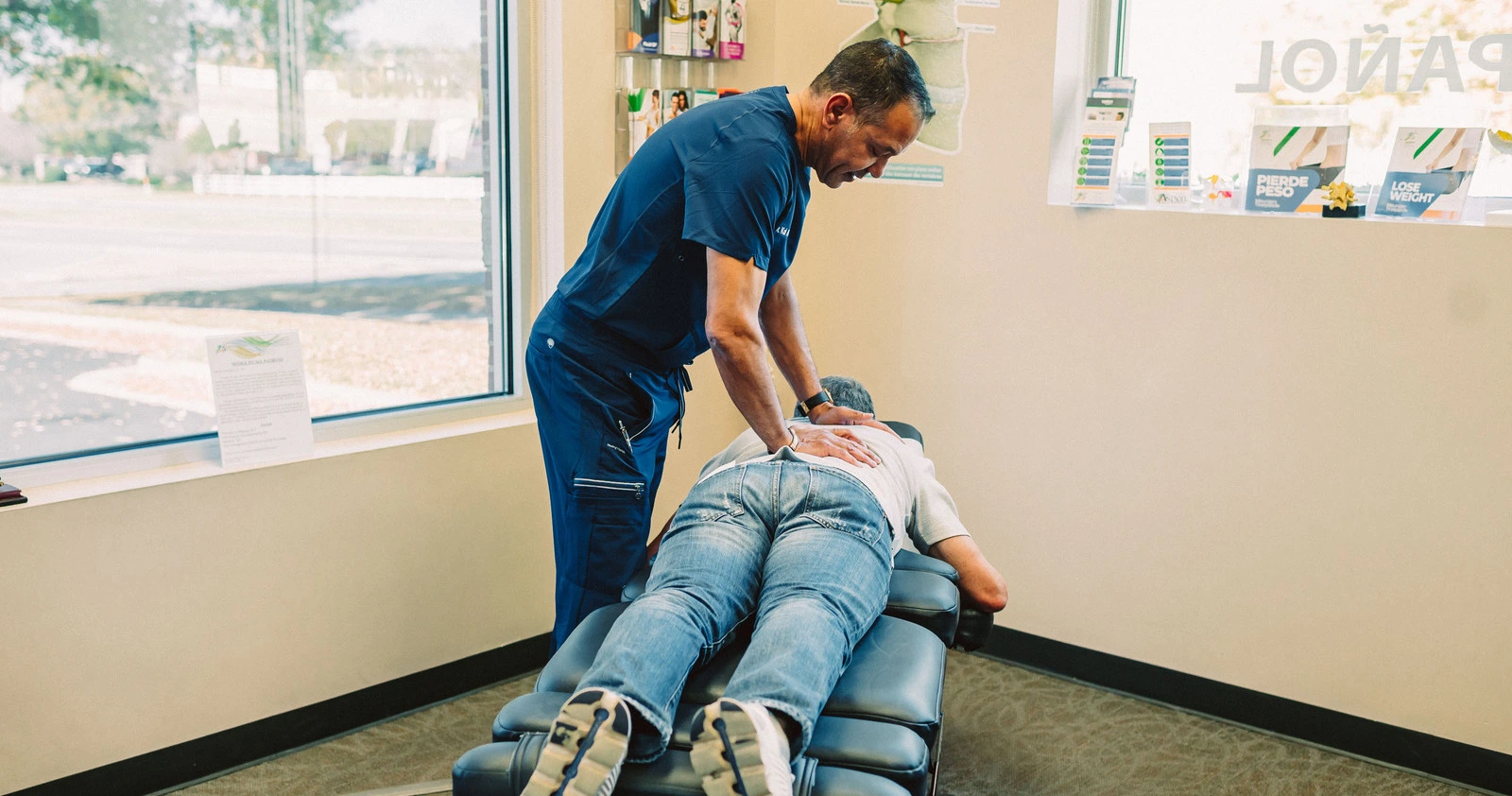
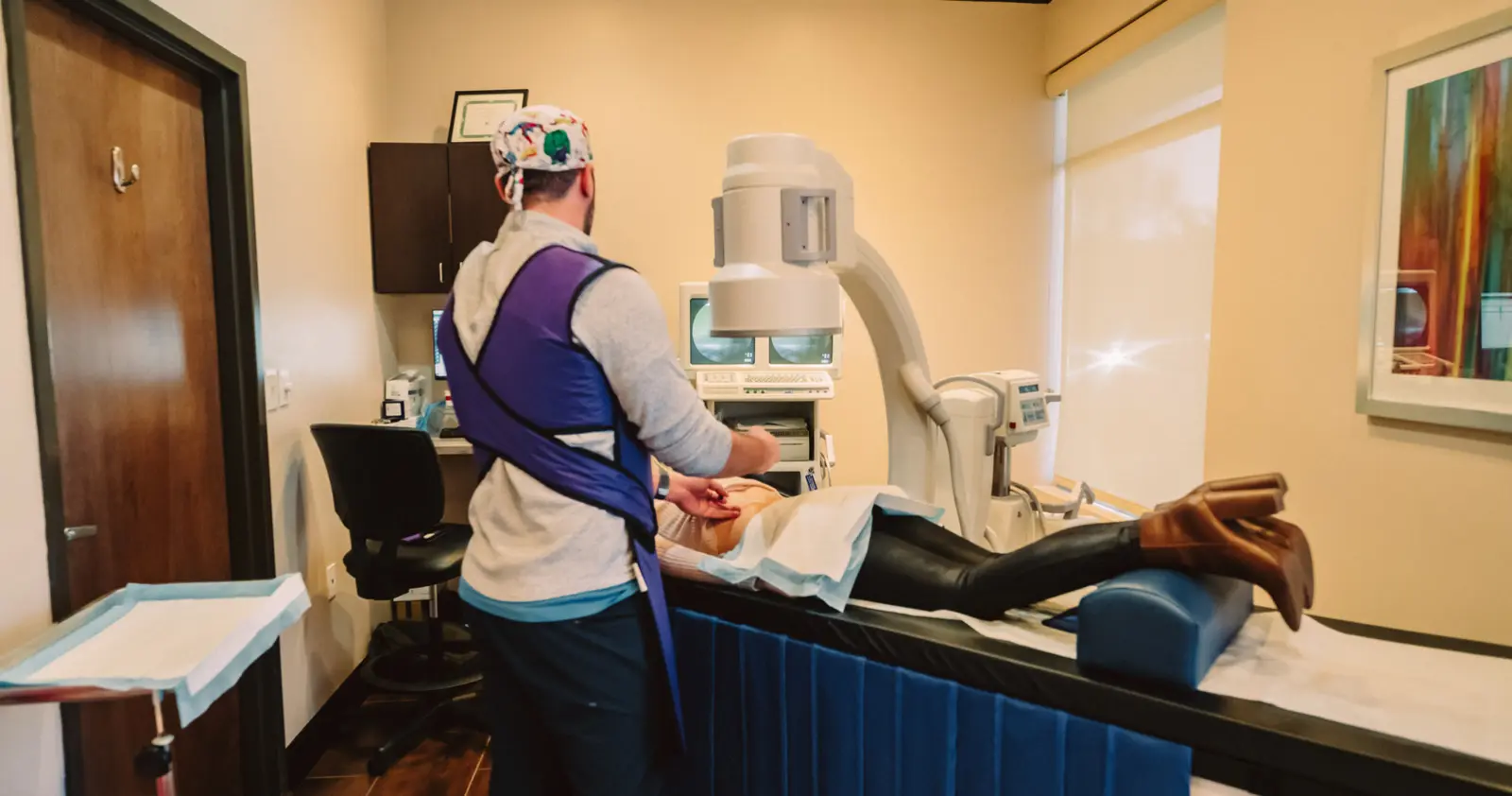
Occasionally, pain can even be the problem without an apparent cause, as in nerve (neuropathic) damage. Neuropathic pain does not have a protective purpose, and there is no known benefit. It may be the result of misread signals between the body’s nerves and the brain, or from damage to a nerve. Call Advanced Health Solutions – GA Spine & Disc now at (770) 926-9495 If you’re experiencing pain that started recently or living with chronic pain, our pain treatment specialists can help you find relief or manage your pain.