Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral Neuropathy refers to the damage to or disease affecting nerves that may impair gland or organ function, movement, sensation, or other different aspects of health, depending on the nerve affected. It can be idiopathic (no known cause) or genetic (present from birth).
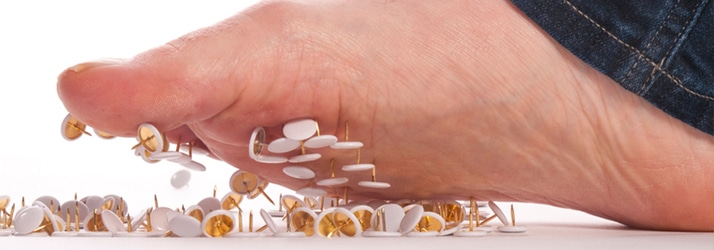
Peripheral neuropathy, resulting from the damage to peripheral nerves, often causes pain, numbness, and weakness, in your feet and hands. It can affect other parts of your body.
Your peripheral nervous system plays a crucial role in sending information from your spinal cord (central nervous system) and brain to the rest of the body. Peripheral neuropathy can result from infections, traumatic injuries, exposure to toxins, inherited causes, and metabolic problems. Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common causes.
People with neuropathy describe the pain as tingling, burning or stabbing. In most cases, symptoms will improve, especially if caused by an eminently treatable condition. Medications reduce the pain of peripheral neuropathy.
Symptoms
Each nerve in the peripheral system has a distinct function. Therefore, symptoms depend on the nerves affected. Nerves are categorized into:
- Autonomic nerves control functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, bladder and digestion
- Motor nerves control muscle movement
- Sensory nerves receive sensation, such as pain, temperature, touch, or vibration from the skin
Signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include:
- Sharp, freezing, jabbing, throbbing or burning pain
- Gradual onset of tingling, prickling or numbness in your hands or feet, which may spread upward into your arms and legs
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Paralysis or muscle weakness due to affected motor nerves
- Falling and lack of coordination
If your autonomic nerves are affected, the signs and symptoms are:
- Altered sweating and heat intolerance
- Bladder, bowel or digestive problems
- Blood pressure changes, causing lightheadedness or dizziness
Peripheral neuropathy affects one nerve (mononeuropathy), two or more nerves in different areas of the body (multiple mononeuropathy) or several nerves (polyneuropathy). People with peripheral neuropathy often have polyneuropathy.
When to See a Woodstock Chiropractor
Seek proper medical care immediately when you notice unusual pain, weakness or tingling in your feet or hands. Early diagnosis and treatment will help to control your symptoms and prevent further damage to peripheral nerves.
Causes
Peripheral neuropathy is not a single disease. It’s nerve damage caused by the following conditions:
- Diabetes – Many people with diabetes develop a type of neuropathy.
- Autoimmune diseases – They include lupus, Sjogren’s syndrome, Guillain-Barre syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, necrotizing vasculitis, and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy.
- Alcoholism – People with alcoholism make poor dietary choices that lead to vitamin deficiencies.
- Exposure to poisons – Toxic substances such as heavy metals.
- Infections – They include certain bacterial or viral infections, including shingles, Lyme disease, Epstein-Barr virus, diphtheria, hepatitis C, leprosy, and HIV.
- Medications – Certain medications such as chemotherapy can cause peripheral neuropathy.
- Inherited disorders – A disorder such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a hereditary type of neuropathy.
- Tumors – Growths, cancerous and noncancerous, develop on the nerves or press nerves. Besides, polyneuropathy arises due to cancers related to the immune response of the body. These are the paraneoplastic syndrome.
- Pressure or trauma on the nerve – Traumas, such as from sports injuries, falls or motor vehicle accidents, can damage or sever peripheral nerves. Nerve pressure can result from using crutches or having a cast, or repetitive motion such as typing many times.
- Bone marrow disorders – These include a form of bone cancer (osteosclerotic myeloma), an abnormal protein in the blood (monoclonal gammopathies), amyloidosis and lymphoma.
- Vitamin deficiencies – Niacin, vitamin E, and B vitamins – including B-12, B-6, and B-1 – are important to nerve health.
- Other diseases – These include liver disease, kidney disease, an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), and connective tissue disorders.

Risk Factors
Peripheral neuropathy risk factors include:
- Diabetes mellitus, especially due to poorly controlled sugar levels
- Abuse of alcohol
- Vitamin deficiencies, mainly B vitamins
- Infections, such as hepatitis C shingles, Lyme disease, Epstein-Barr virus, and HIV
- Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, in which the immune system attacks its tissues
- Exposure to toxins
- Liver, thyroid or kidney disorders
- Repetitive motion, such as typing
- Family’s neuropathy history
Complications
Complications of neuropathy include:
- Skin trauma and burns – You may not feel pain or temperature changes on parts of your body that are numb.
- Falls – Loss of sensation and weakness may be associated with falling and lack of balance.
- Infections – Your feet and other areas of the body lack sensation and become injured without your knowing. Check the areas on a regular basis and treat any minor injuries to avoid infection, especially if you’ve diabetes mellitus.
Diagnosis
Peripheral neuropathy has several causes. Besides a physical examination that can include blood tests, diagnosis requires:
- A full medical history – Dr. Kal will review your medical history, including a family history of the nervous system (neurological) diseases, your symptoms, exposure to toxins, drinking habits and your lifestyle.
- Neurological examination – Your chiropractor may check your muscle tone and strength, your tendon reflexes, your posture and coordination, and your ability to feel sensations.
- Your chiropractor may order the following tests:
- Imaging tests – MRI or CT scans can look for herniated tumors, disks or other abnormalities.
- Blood tests – They detect abnormal immune function, vitamin deficiencies, diabetes and other indications of conditions, which can cause peripheral neuropathy.
- Other nerve function tests – These can include a sweat test, an autonomic reflex screen, recording how your autonomic nerve fibers work, and sensory tests recording how you feel heat, cooling, touch, and vibration.
- Nerve function tests – Electromyography can record electrical activity in your muscles. It helps to detect nerve damage. A probe sends electrical signals to your nerve, and an electrode placed along the pathway of the nerve records the response to the signals.
- Skin biopsy – Your doctor will remove a small portion of your skin to look for the reduction in nerve endings.
- Nerve biopsy – It involves the removal of a small portion of a nerve, such as sensory nerve, to look for any abnormalities.
Treatment
The goals of the treatment are to manage the condition(s) causing your peripheral neuropathy and relieve its symptoms. If your laboratory tests show no underlying condition, your chiropractor may recommend watchful waiting to check if your peripheral neuropathy improves.
Neuropathy Treatment Using TeslaMax
TeslaMax is a revolutionary technology for neuropathy relief that’s changing lives across the US and the world. TeslaMax uses a proprietary form of AC (alternating current) to stimulate deep, painless muscle contractions in peripheral neuropathy-affected areas.
The muscle contractions improve lymphatic drainage, increase local circulation, and stimulate your nerves — all of which boost your body’s natural ability to repair the damaged nerves. DC (Direct Current)-based muscle stimulators and other muscle stim units use DC at higher amperage levels that can painfully sting and burn your skin while stimulating weak muscle contractions.
On the other hand, TeslaMax uses Tesla-Based technology to penetrate the deepest muscle fibers for a remarkable experience that’s unlike anything you’ve tried before. It’s difficult to understand the profound difference between the TeslaMax and other neuropathy therapies until you try it.
Why Use the TeslaMax for Peripheral Neuropathy?
Muscle stimulators can’t create anything more than weak muscle contractions, but TeslaMax is quite different. TeslaMax uses proprietary Tesla-Based Technology to stimulate very strong — but totally painless — muscle contractions in your feet, legs, and other areas affected by neuropathy.
The deep muscle contractions significantly remove excess fluid build-up (edema) and improve local circulation. Pushing out edema and restoring healthy blood flow provides an ideal environment for your body to repair nerve damage that causes peripheral neuropathy.
The deeper the muscle contractions, the more dramatic the improvement in lymphatic drainage and blood flow; that is precisely what you get with TeslaMax.

Preparing For Your Appointment
You may begin by seeing your primary care provider; then you make an appointment with a Woodstock chiropractor trained in nervous system disorders.
Here is crucial information to help you prepare for your appointment.
What You Can Do
When you make an appointment, ask if there is anything you should do in advance, such as fasting for a particular test. Make a list of:
- Key personal information, including major life changes or recent stresses, alcohol use and family medical history
- Your symptoms, including those that may seem unrelated to the purpose of your appointment
- All medications, vitamins or other supplements, including doses
- Questions to ask your chiropractor
If possible, take a friend or family member along who can help you remember the information you are given.
Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy
For peripheral neuropathy, questions to ask your chiropractor include:
- What is the likely cause of my symptoms?
- Are there other possible causes?
- Do I need any tests?
- Is this condition long-lasting or temporary?
- What are the available treatments, and which do you recommend?
- What are the side effects of the treatment?
- Are there alternatives to the approach you are suggesting?
- I’ve other health conditions. How do I manage them together?
- Do I have to restrict activities?
Do not hesitate to ask other relevant questions.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Your chiropractor will likely ask you the following questions:
- Do you’ve health conditions, such as kidney disease or diabetes?
- When did your symptoms start?
- Does anyone in your family have similar symptoms?
- Have your symptoms been occasional or continuous?
- How severe are the symptoms?
- What seems to improve your symptoms?
- What, if anything, seems to worsen your symptoms?