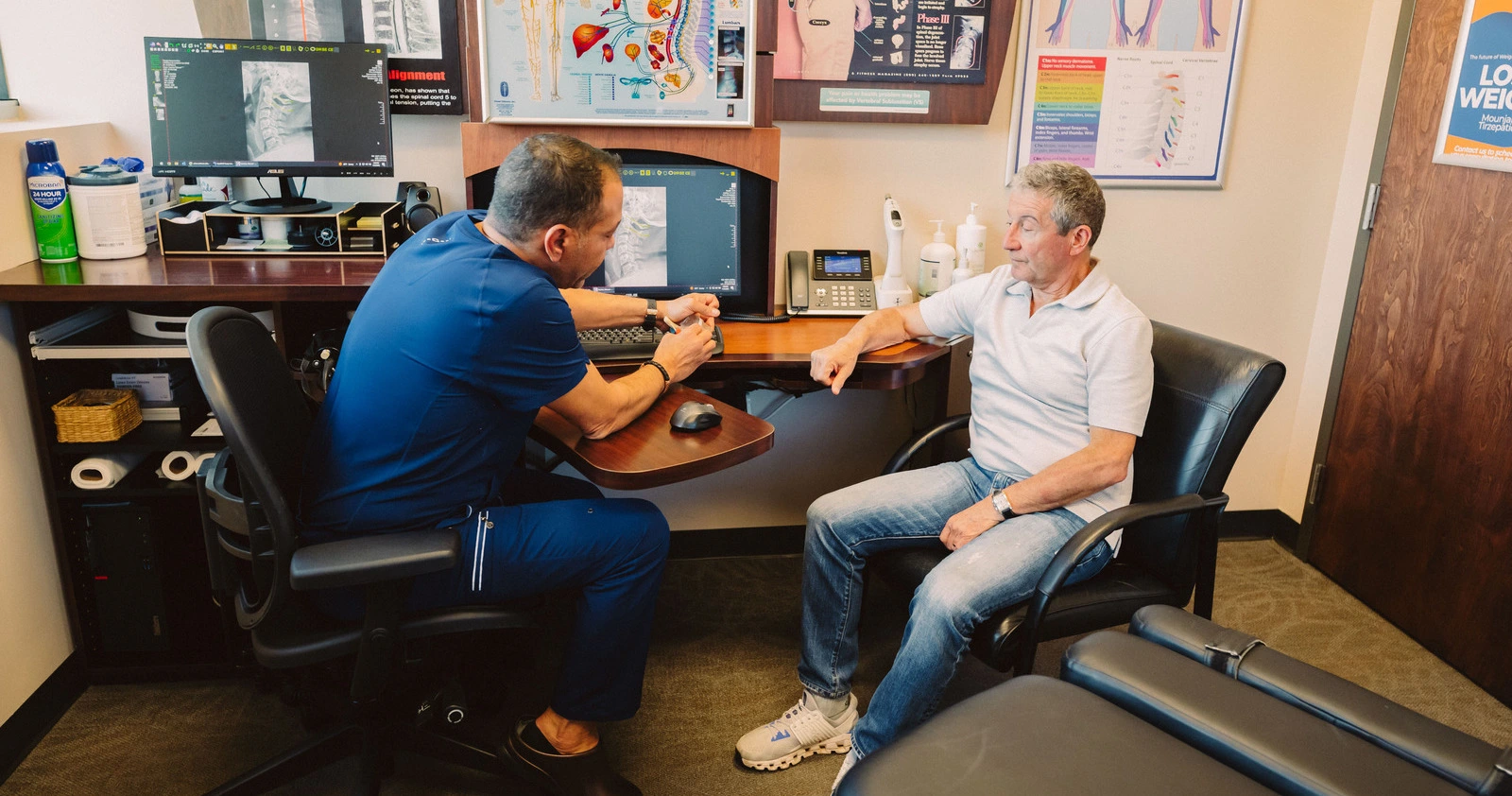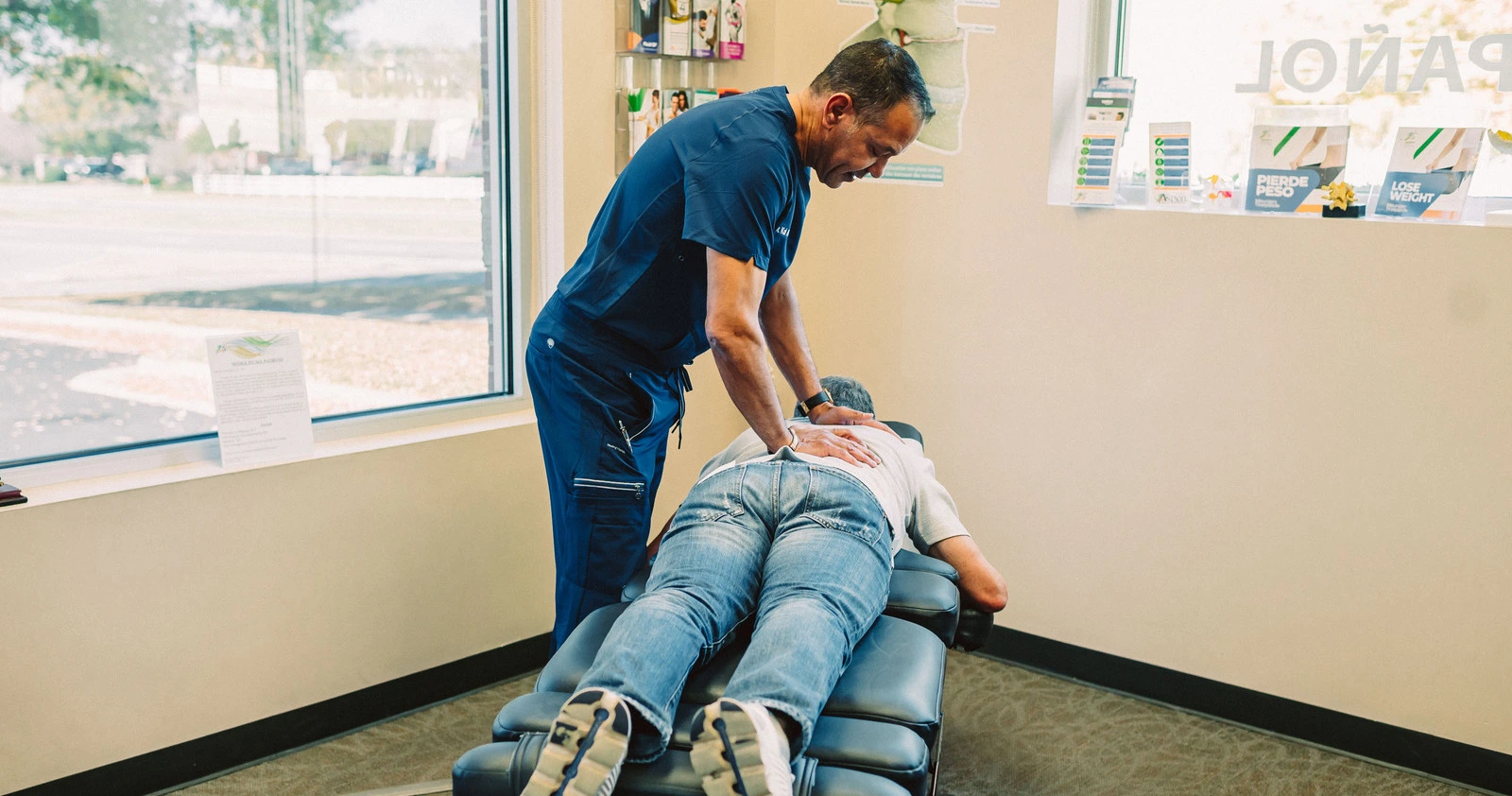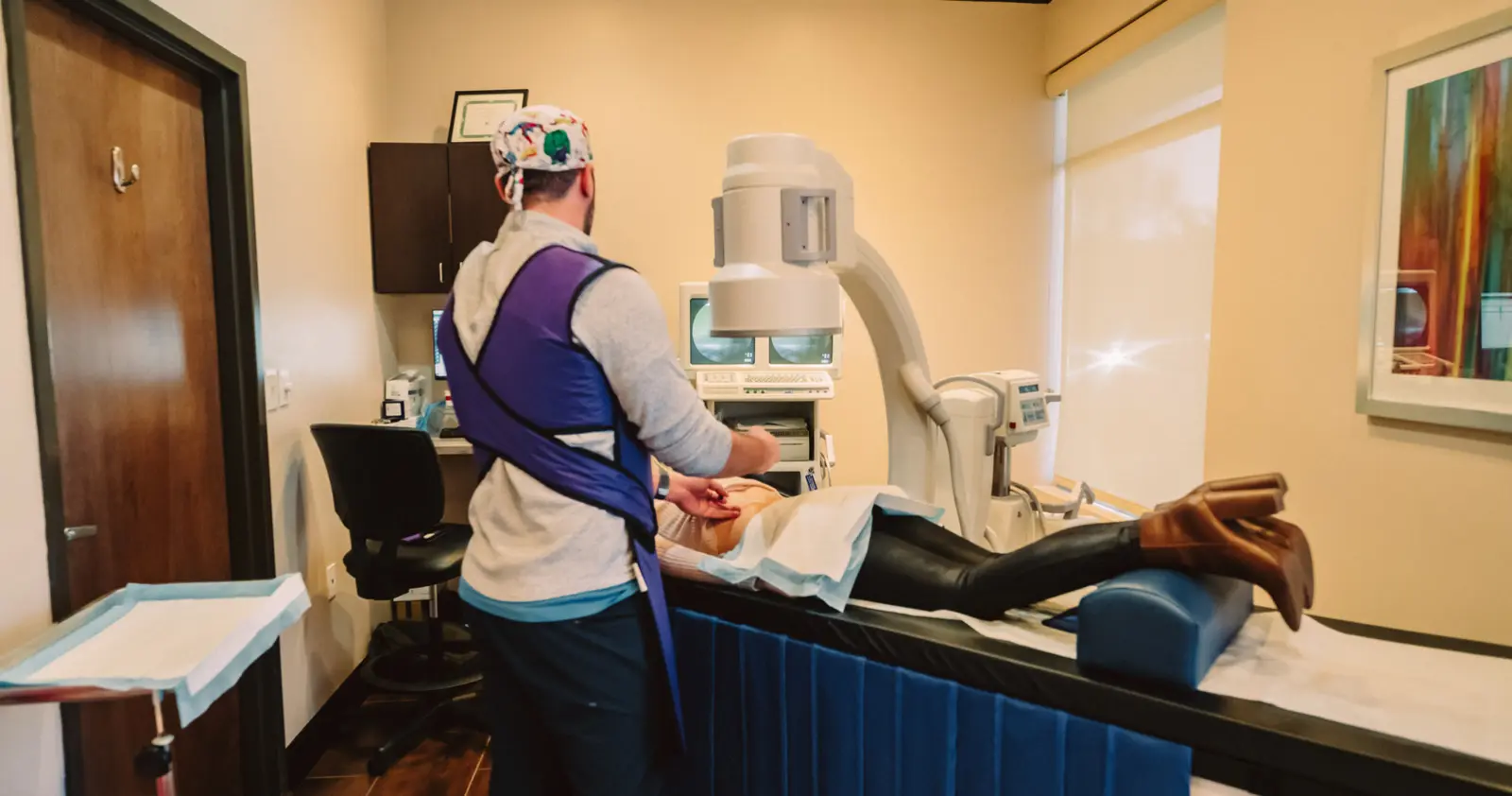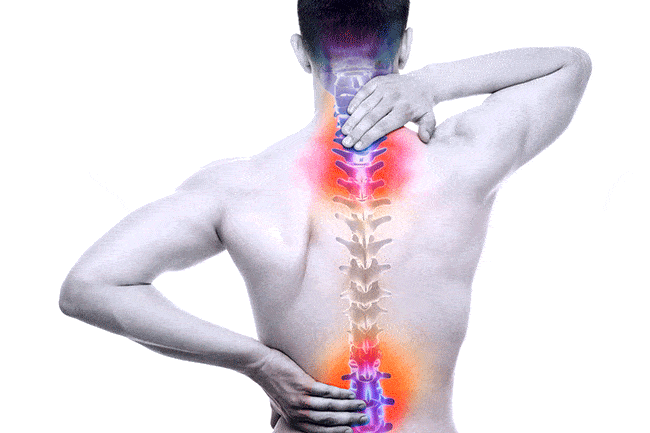
Degenerative disc disease can cause a reduction in the elasticity and height of intervertebral discs. Over time, a disc may bulge or herniate, causing tingling, numbness, and pain that runs into the arm. Visit Advanced Health Solutions – GA Spine & Disc ,or contact us at (770) 926-9495 We offer high-quality chiropractic care for neck pain that is tailored to meet the individual patient’s needs.